About us
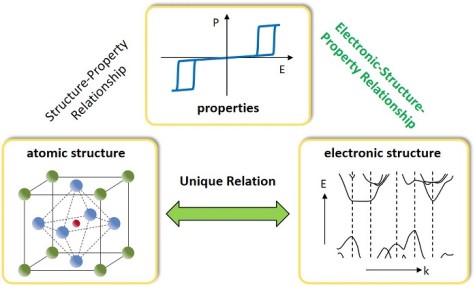
The electronic structure of materials determines their electrical, optical, mechanical and many other properties. We are aiming at finding the correlations between the electronic structure of materials and their functional properties. Our current emphasis is on metal oxides including electronically and ionically conducting as well as dielectric oxides with applications in energy conversion and storage systems such as solar cells, displays, capacitors and fuel cells. Defects and interfaces are particularly important in these systems.

News
-
![]()
![]()
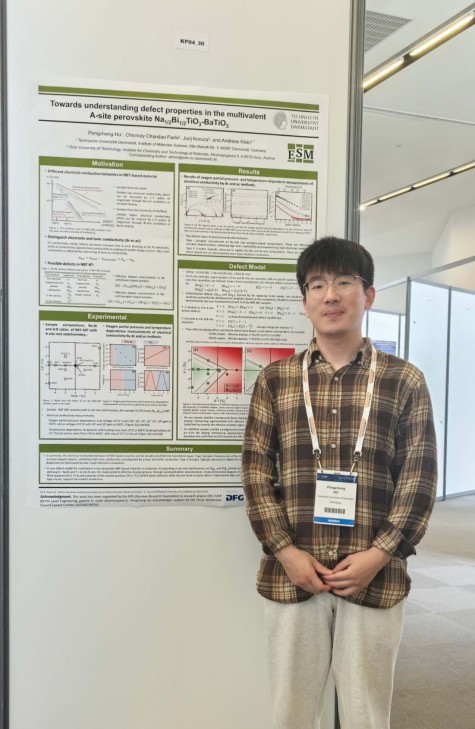
Poster Prize for Pengcheng Hu
June 04, 2025
At the E-MRS Spring Meeting 2025 in Strasbourg
-
![]()
![]()
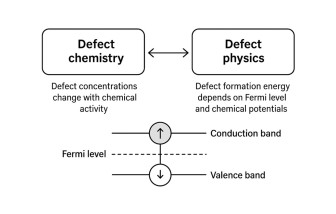
The physics of defect chemistry and the chemistry of defect physics
April 15, 2025
New Publication
This tutorial-article explores two ways of looking at defects in solids. One perspective, called defect chemistry, treats them with chemical reaction rules: concentrations of defects change depending on the chemical environment, and everything must balance in terms of charge and atoms. The other perspective, defect physics, uses thermodynamics and quantum mechanics to calculate how much energy is needed to form a defect. This energy depends on both the position of the Fermi level and the chemical environment.