(S)TEM Investigation of the Atomic Structure and Domain Morphology of Anti-Ferroelectric Ceramics
Project Members
Hui Ding (PhD Student), Leopoldo Molina-Luna (PI) and Hans-Joachim Kleebe (PI)
Description
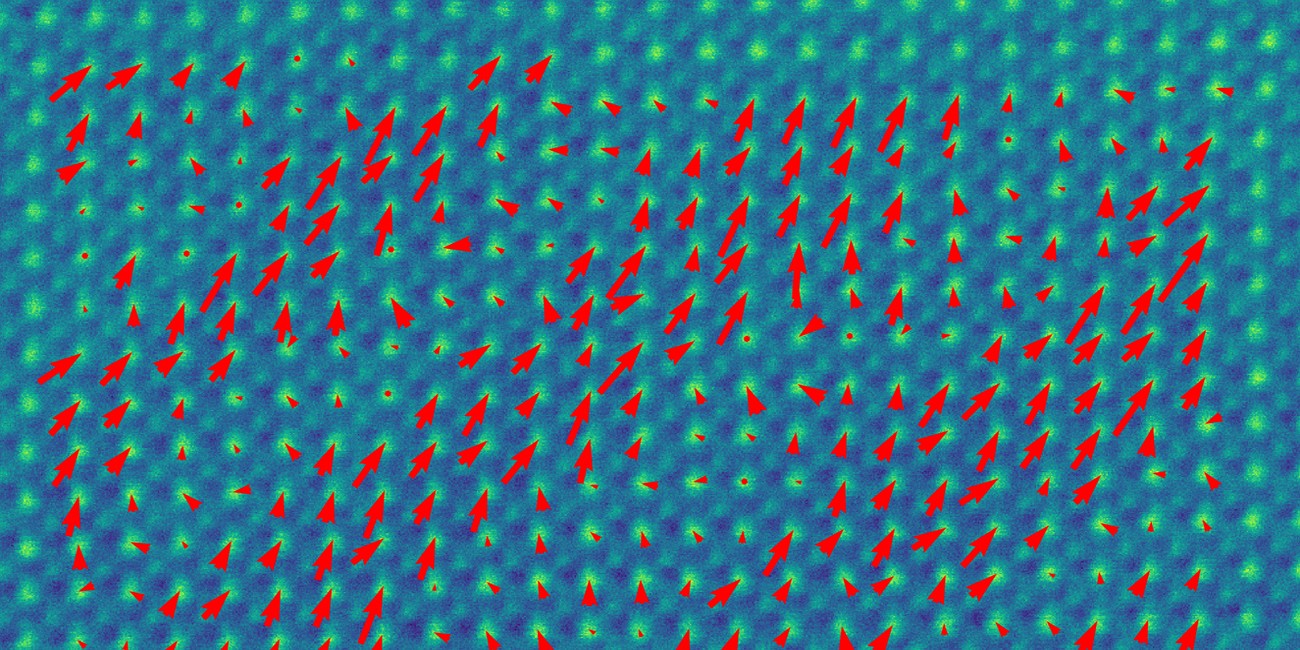
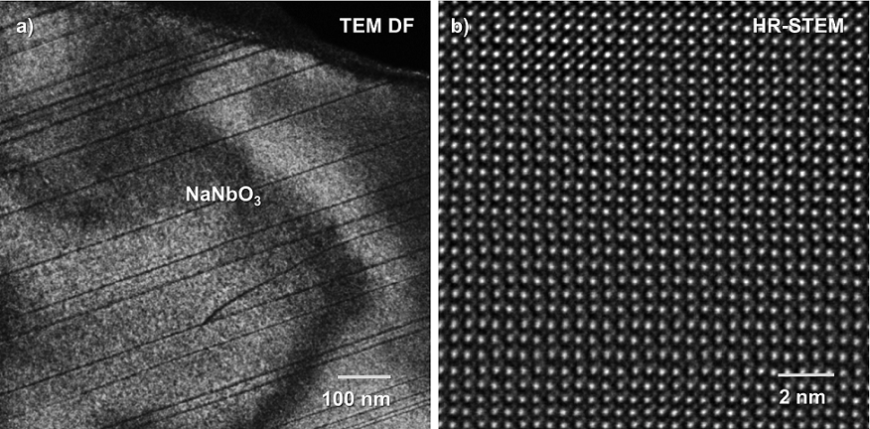
Antiferroelectrics (AFE) have great advantages in the application for energy storage devices for the reversible phase transitions between AFE and ferroelectric (FE) states. As prototype AFEs, lead containing PbZrO3 (PZ) and lead-free NaNbO3 (NN) are investigated by conventional transmission electron microscopy (TEM), using electron diffraction and bright field and dark field imaging techniques to reveal the domain morphology and crystallography. To enhance the energy storage property, several doped AFEs or solid solutions based on PZ and NN have been developed, for instance (Pb,La)(Zr,Sn,Ti)O3 and NaNbO3 – SrSnO3 series and then investigated by TEM as well. Furthermore, scanning TEM (STEM) is employed to reveal the atomically resolved structure and local displacement vectors of the central atom (polarization map) in PZ and NN.
The LOEWE project FLAME
The goal of the project is to use electronic structure analysis to identify new lead-free antiferroelectric materials