Domain size and charge defects on the polarization switching of antiferroelectric domains
New Publication in “Chinese Physics B”
2023/07/25
Authors: Jinghao Zhu, Zhen Liu, Boyi Zhong, Yaojin Wang and Baixiang Xu
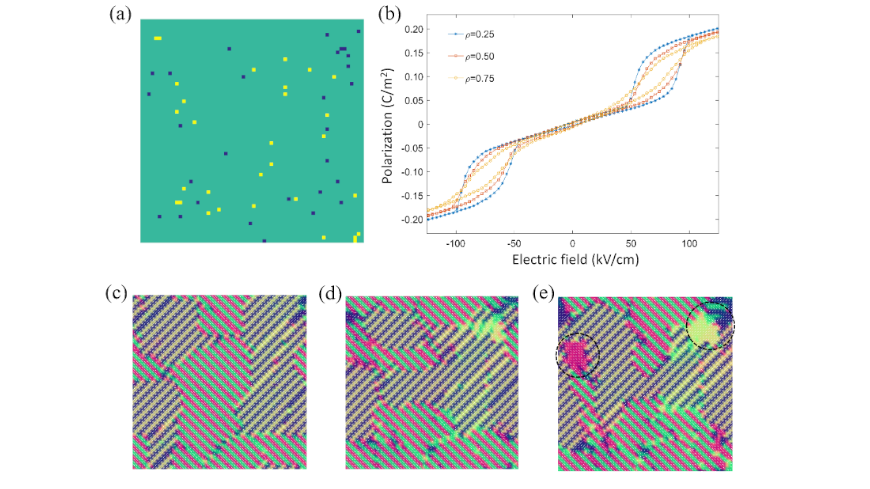
The switching behavior of antiferroelectric domain structures under the applied electric field is not fully understood. In this work, by using the phase field simulation, we have studied the polarization switching property of antiferroelectric domains. Our results indicate that the ferroelectric domains nucleate preferably at the boundaries of the antiferroelectric domains, and antiferroelectrics with larger initial domain sizes possess a higher coercive electric field as demonstrated by hysteresis loops. Moreover, we introduce charge defects into the sample and numerically investigate their influence. It is also shown that charge defects can induce local ferroelectric domains, which could suppress the saturation polarization and narrow the enclosed area of the hysteresis loop. Our results give insights into understanding the antiferroelectric phase transformation and optimizing the energy storage property in experiments.
Link to Article
Chinese Physics B, vol. 32, no. 4, p. 47701, Apr. 2023



