Impact of interface structure on magnetic exchange coupling in MnBi/FexCo1−x bilayers
New Publication in “Physical Review B”
2018/11/29
Authors: S. Sabet, A. Moradabadi, S. Gorji, M. Yi, Q. Gong, M. H. Fawey, E. Hildebrandt, D. Wang, H. Zhang, B.-X. Xu, C. Kübel, and L. Alff
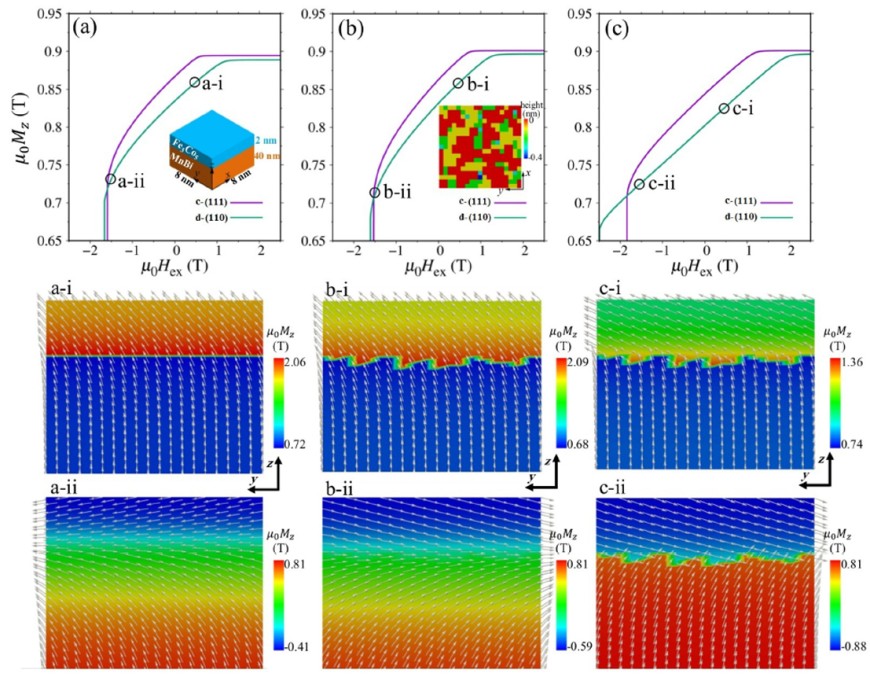
Magnetic exchange coupling behavior was investigated in MnBi/FeCo bilayer system at the hard/soft magnetic interface. We performed a combined study of cross-sectional high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), DFT calculations, and micromagnetic simulations to elucidate effect of interface structure on exchange coupling. Exchange spring MnBi/FexCo1−x(x=0.65 and 0.35) bilayers with various thicknesses of the soft magnetic layer were deposited in a dc magnetron sputtering unit from alloy targets. According to magnetic measurements, using a Co-rich layer leads to a more coherent exchange coupling with optimum soft layer thickness of about 1 nm. Our DFT calculations predicted formation of a polycrystalline FeCo layer with coexisting crystalline and disordered (110) phases. The indexed FFTs from HR-TEM images confirmed a crystalline FeCo(110) layer, with slight misorientation in some areas, and a disordered region close to the interface which deteriorates interface exchange coupling. Moreover, our micromagnetic simulations showed how the thickness of the FeCo layer and the interface roughness both control the effectiveness of exchange coupling in MnBi/FeCo bilayer.



