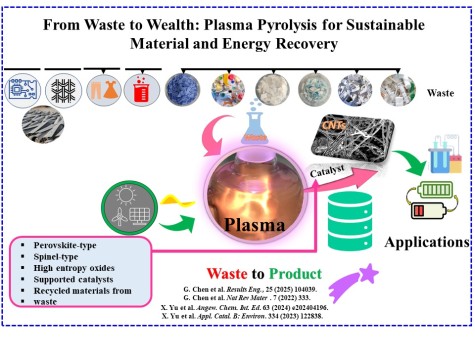
Plasma-based technologies offer a transformative solution for waste management and resource recovery by converting waste into sustainable chemicals and fuels. This approach fosters circular and eco-friendly economies by utilizing plasma’s highly reactive species and energetic electrons to decompose complex waste materials into valuable chemical feedstocks and functional materials. Plasma pyrolysis has demonstrated exceptional versatility in recycling diverse waste streams, including plastics, rubber, liquid waste, textile waste, fiber-reinforced composites, and electronic waste. Unlike conventional recycling methods, plasma pyrolysis can be rapidly switched on and off, making it compatible with fluctuating renewable energy sources like wind and solar power. This flexibility enhances its efficiency and environmental benefits.
A key advancement in this field is the integration of plasma pyrolysis with thermal catalytic pyrolysis, creating a hybrid system that improves waste conversion efficiency. The incorporation of catalytically active materials is essential for optimizing the selectivity and yield of chemical products such as H2 and C2H2 while also promoting the synthesis of high-value carbon nanomaterials. By fine-tuning catalyst design and process conditions, this approach maximizes the generation of valuable outputs. Among the most promising products generated through plasma pyrolysis are Carbon Nanotube Composite (CNC) materials, known for their exceptional electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties. These advanced materials hold great potential for energy storage applications, particularly in lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries and solid oxide cells (SOCs), where they contribute to improved performance and efficiency.
By advancing catalyst development and optimizing reaction conditions, plasma-enabled pyrolysis offers a scalable and sustainable solution to global waste management challenges. This technology aligns with circular economy principles, facilitating the shift from waste disposal to resource recovery and the production of high-value materials.