Modelling of Quartz
A machine-learned interatomic potential for silica and its relation to empirical models
2022/07/28 by K. Albe
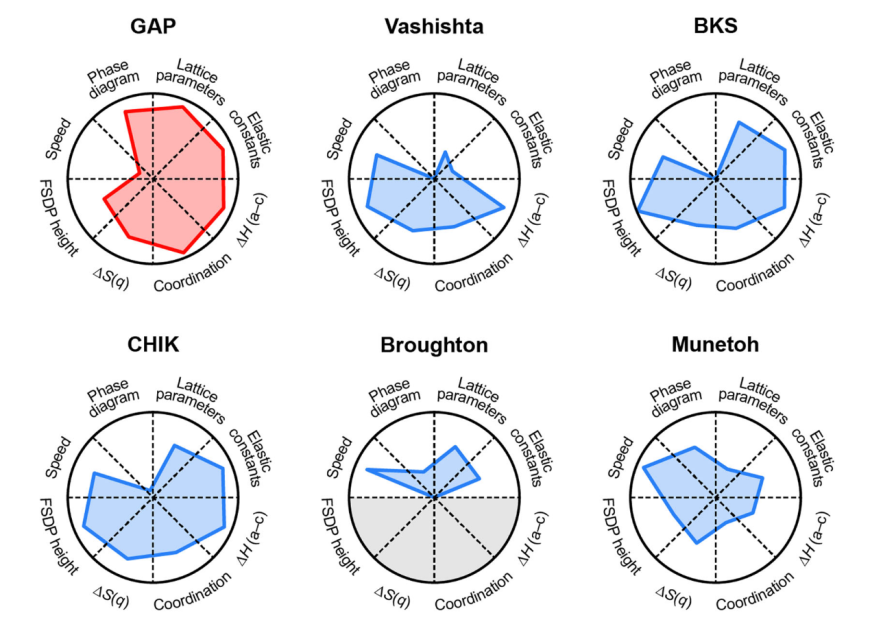
In the present work, we surpass the limitations of currently available silica potentials by training an ML potential for a range of crystalline polymorphs as well as models for liquid and amorphous phases. The potential shows high thermodynamic accuracy, enabled by the use of the strongly constrained and appropriately normed (SCAN) functional of Sun et al.43 for the computation of reference data. Thus, the ML potential shows superior behaviour in predictions of phase coexistence lines and high-pressure structural transitions compared to several existing, empirically fitted interatomic potentials. The results also allow us to discuss, more generally, the criteria for evaluating the quality of an ML potential—thereby placing it in the context of more established simulation methods in terms of their computational cost, predictive power, and applicability to practical research questions.



